Once the invoice is issued in a later accounting period, the entry could be reversed by crediting the accounts receivable and debiting the accrued revenue account. Since most prepaid contracts are less than one year long, unearned revenue is generally a current liability. Sometimes you are paid for goods or services before you provide those services to your customer.
- Prepaid insurance received by theinsurance company creates a liability for the insurance company but that is unearnedrevenue.
- This is crucial in building trust among investors, shareholders, and other stakeholders.
- Once the invoice is issued in a later accounting period, the entry could be reversed by crediting the accounts receivable and debiting the accrued revenue account.
- It is classified as a current liability until the goods or services have been delivered to the customer, after which it must be converted into revenue.
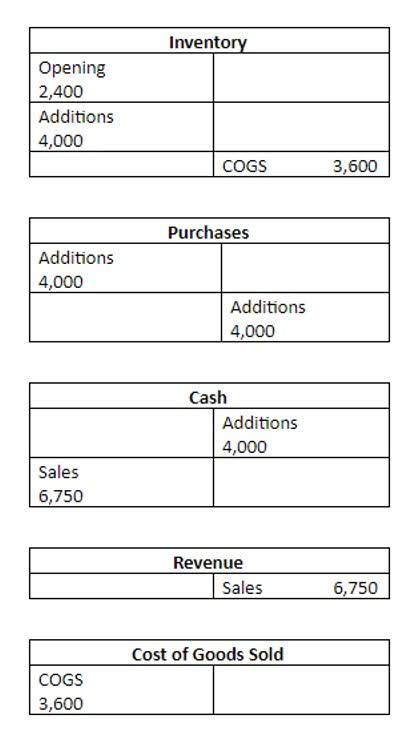
- Therefore, the journal entry to record unearned revenues is as follows.
- This section will discuss necessary adjustments and handling overstatements and understatements.
Almost all the time, unearned revenues are short-term as customers don’t pay for goods or services beforehand in the long term. Therefore, companies must classify unearned revenues as current liabilities. However, in cases where a company receives money for sales that it expects to make after a year, it can also classify unearned revenues as non-current liabilities. The company will debit the cash account while credit the current liability account, balancing the financial statements. When the ABC Company gradually delivers the service to the customer for parking, they will recognize the unearned revenue in the revenue account.
For example, if your startup signs multiple annual contracts in Q1, your bookings and cash flow spike — but your recognized revenue remains modest. By managing and reporting deferred revenue properly, CFOs ensure transparency and build investor trust. Beyond compliance, deferred revenue signals a customer’s commitment to your product. It demonstrates that the company has locked in revenue that will be earned over time, which supports accurate budgeting, headcount planning, and investor messaging.
AccountingTools
Under ASC 606, businesses must recognize revenue only when they complete a service or deliver a product. If they record revenue too early, they risk SEC investigations, financial restatements, and investor concerns. Deferred revenue is not just a balance sheet item — it’s a forward-looking, strategic KPI that helps SaaS startups communicate stability, plan growth, and manage investor expectations.
The accounting standards require companies to record unearned revenues as liabilities and not as actual revenues. Unearned revenues refer to any funds that companies receive for future sales. While referred to as unearned revenues, they do not represent revenues at all. It is because accounting standards don’t allow companies to record revenues unless they meet performance obligations.
Balance sheet
Clear disclosure helps ensure transparency and accurate financial reporting for investors and other stakeholders. Unearned revenue does not initially appear on a company’s income statement. As the company fulfills its obligation how to start a profitable vending machine business to provide the goods or services, the unearned revenue liability is decreased, and the revenue is recognized on the income statement.
Unearned revenue, also known as deferred revenue or prepaid revenue, is money received by a company for a service or product that has yet to be provided or delivered. This type of revenue is recorded as a liability because the company owes the delivery of goods or services to its customers. Unearned revenue, also known as deferred revenue, is a crucial element in a company’s financial statements. It represents the money received by a company for goods or services that have not yet been delivered.
- Understanding why customers leave, using data and insights, is the first step to retaining them.
- Similarly, businesses require customer deposits for reservations, event bookings, or large purchases.
- Another trend is pairing deferred revenue with metrics like Net Revenue Retention (NRR) and billings to get a complete view of sales momentum.
- For example, a law firm may charge a $10,000 retainer for legal representation.
- Sometimes you are paid for goods or services before you provide those services to your customer.
- Small business owners must determine how best to manage and report unearned revenue within their accounting journals.
Businesses accept unearned revenue because upfront payments provide financial stability and reduce risk. Customers often pay in advance for products or services to secure availability, lock in pricing, or meet contract terms. This allows companies to plan ahead, allocate resources, and operate without relying on credit or uncertain future sales.
Unearned Revenue Journal Entries
Unearned revenue is listed under “current liabilities.” It is part of the total current liabilities as well as total liabilities. For example, a law firm may charge a $10,000 retainer for legal representation. The firm holds this amount as unearned revenue and deducts from it as they complete billable work. If the entire amount isn’t used, the firm may refund the client or apply the remaining balance to future services. This ensures accurate and timely reporting aligned with regulatory guidelines.
Entire unearned revenue liability will be set off against revenue only when the value of services provided is equal to the unearned revenue liability account. Unearned revenues are useful for the seller for the cash flow performance because they have already received the cash while no service has been provided yet. Even if the company performs all its obligations and has earned the revenue per the accounting principle, it can’t record the income in the current period, resulting in unrecorded revenue.
What is the correct method to record an entry of unearned revenue in accounting?
A subscription-based business charges customers on a recurring basis for continued access to a product what is invoice factoring or service. This model is common in streaming platforms (Netflix, Spotify), SaaS companies (Microsoft 365, Salesforce), gyms, and online memberships. Similarly, unearned revenue can affect the debt-to-equity ratio, a measure of financial leverage.
Unearned Revenue: Decoding Its Significance in Business Accounting
Unearned revenue is most common among companies selling subscription-based products or other services that require prepayments. Classic examples include rent payments made in advance, prepaid insurance, legal retainers, airline tickets, prepayment for newspaper subscriptions, and annual prepayment for the use of software. These standards ensure consistency and transparency in financial reporting, enabling investors and analysts to make informed decisions.
Publishing and Prepaid Services
Unearned revenue and deferred revenue are mostly used differently but it is referred to as the same thing. This is the cash received by the seller or the company, but they have not yet performed their duties, or their performance is not satisfied by the customer yet. Accordingly, on April 30, another journal entry will be added to reflect the earnedincome for this month. Since they overlap perfectly, you can debit the cash journal and credit the revenue journal. In this situation, unearned means you have received money from a customer, but you still owe them your services. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) that a public company must meet to recognize revenue.
In conclusion, the proper accounting treatment of what is form 8941 its a tax credit for small business health insurance costs unearned revenue is necessary for accurate representation of a company’s financial health. Unearned revenue should be entered into your journal as a credit to the unearned revenue account and as a debit to the cash account. This journal entry illustrates that your business has received cash for its service that is earned on credit and considered a prepayment for future goods or services rendered. Unearned revenue is money received by a business for goods or services that have not yet been delivered.
The payment represents a company’s obligation to deliver a product or service in the future. Many businesses collect payments before delivering a product or service. Whether it’s a retainer for a lawyer, a deposit on a new car, or a prepaid gym membership, these advance payments give businesses financial security while creating an obligation to fulfill. Companies across industries, from retail and software to professional services, handle unearned revenue daily. Companies track unearned revenue through detailed systems to ensure accurate reporting and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Unearned revenue, also known as deferred revenue or prepaid revenue, refers to the payments received by a company for goods or services that are yet to be delivered or provided. It is recorded as a liability on the company’s balance sheet because the company owes the delivery of the product or service to the customer. Examples of industries dealing with unearned revenue include Software as a Service (SaaS), subscription-based products, airline tickets, and advance payments for services.
When the products or services are delivered over time to customers, they are recognized as revenue gradually in the income statement. Unearned revenue is recorded as liabilities when the cash is received. These liabilities amount will be released/derecognized simultaneously with the revenues recognition when the performance obligation is met.